Ransomware? What it is

Ransomware, a malicious software which locks data on victim’s computer typically using encryption which blocks access to data unless the victim pays the ransom. unlike other attacks, the victim is notified that exploitation of data has occurred. Additionally, criminals provide instruction to the victim to recover after they receive payment for decryption in the form of virtual currency like Bitcoin, so the identity of criminal remain unknown. Sometimes Criminal change the login credentials of the victim’s device and demand ransom for it.
Ransomware attack is growing at a yearly rate of 350 percent. According to reports by the end of 2017 global damage because of ransomware attack stood at nearly $5Bn and according to some Cybersecurity ventures it will cross the mark of $6trillion annually by 2021, this is an alarming data.Additionally, Cybersecurity spending will grow to $1trillion within next four years.
How Computer gets Ransomware?
Typically spread through phishing emails that contain malicious attachments or though drive-by downloading which occurs when a user visits a malicious website which downloads and install malware without user’s knowledge. Additionally, newer methods of ransomware infection have been observed, which help criminals to send malware using social media and even using vulnerable web servers, growing number of attacks have used remote desktop protocol and other approaches that don’t rely on any form of user interaction.
Ransomware subcategories:
- The file-encrypting Ransomware: this malicious subcategory’s representatives may be used for data encryption and the subsequent demands of a ransom. This is perhaps the most horrifying subtype of Ransomware you could ever get to know.
- Ransomware used for blocking the screens of your mobile devices: no matter what sort of a portable device you own – a tablet, a phone or a laptop, you may catch such a version of Ransomware. Fortunately, in such a case, no files will get encoded, only your screen will be blocked. Actually, the message displayed, demanding the ransom on the whole screen is the thing that makes you unable to access any icon or shortcut. In fact, that’s why the hackers want you to pay a ransom – for the removal of the cheeky pop-up covering your screen and stopping you from using your device.
Some Famous Ransome Attacks
1. Cryptolocker:
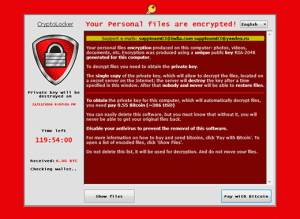
The first example of widely spread Ransome attack using public-key encryption was Cryptolocker, a Trojan Horse malware launched from September 2013 through May of following year. The malware demanded payment in form of either Bitcoin or in prepaid vouchers and experts believed that it used RSA cryptography and was impenetrable. However, a security firm gained access to control server used by the attack and recovered the encryption keys. An online tool was provided to victims for free key recovery to defang the attack.
2. WannaCry:
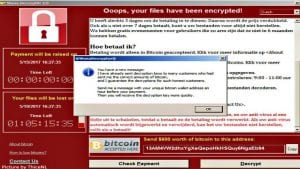
Was a worldwide attack that targeted thousands of computer in over 150 countries. Hard drive content of computer was infected by the malware and then WannaCry executers demanded payment in Bitcoin to unlock them.The Attack was considered the worst cyber attack, not because of its widespread impact but also exploited the vulnerability of Microsoft Windows operating system using code, called EternalBlue developed by US National Security Agency, which was stolen and leaked to the world by a group called TheShadowBrokers.
3. TorrentLocker:
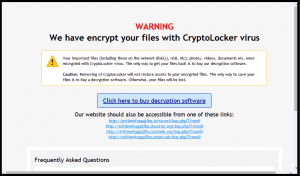
Generally distributed through spam email campaigns and geographically targeted with email messages delivered to specific regions. TorrentLocker often referred to as CryptoLocker, and it uses an AES algorithm to encrypt file types. In addition to encoding files, it also collects email addresses from the victim’s address book to spread malware beyond the initially infected computer—this is unique to TorrentLocker.
4. Petya:

Released in 2016, Unlike other ransomware listed, Petya doesn’t mess around with file encryption, instead, it targets whole computer systems. For a Petya attack to be successful it will need to overwrite the Master Boot Record (MBR), causing a full blue screen of death crash. This will mean, when the victim turns on their machine, they met with a skull and crossbones landing page and of course a ransom note.
5. GandCrab:
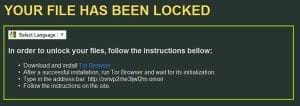
Released in January, this year. GandCrab has some interesting features not seen before in a ransomware, such as being the first to accept the DASH currency and the first to utilize the Namecoin powered .BIT ltd. Phishing emails feature common subjects about payments, tickets, invoices and orders and contain a Javascript attachment which when executed, downloads GandCrab from a malicious URL. Infected systems are directed to a site that can only be accessed through Tor browser, where they can “purchase” a private key to decrypt the files. When it comes to successful infections, the US currently accounts for the fourth largest percentage of victims, behind Peru, Chile and India.
And many more…
Tips To Prevent Ransomware Attack
- Keep clear inventories of all of your digital assets and their locations, so cybercriminals do not attack a system you are unaware of.
- Keep all software up to date, including operating systems and applications.
- Back up all information every day, including information on employee devices, so you can restore encrypted data if attacked.
- Back up all information to a secure, offsite location.
- Segment your network: Don’t place all data on one file share accessed by everyone in the company.
- Train staff on cybersecurity practices, emphasizing not opening attachments or links from unknown sources.
- Develop a communication strategy to inform employees if a virus reaches the company network.
- Perform a threat analysis in communication with vendors to go over the cybersecurity throughout the lifecycle of a particular device or application.
- Instruct information security teams to perform penetration testing to find any vulnerabilities.
- Always use Virtual Private Network (VPN) when accessing public Wi-fi, to safeguard your privacy.
Protecting against ransomware can be difficult since attackers actively alter their programs to defeat detection. However, antivirus is still one of the best methods to protect yourself against known ransomware in the wild. And follow the above-given tips to prevent yourself to be a victim for ransom and be safe in the online world.
Also read our previous article on best backup software to safeguard your data in Microsoft windows.





