For those of you who have recently bought mobile phones or have compared the specifications of some of them, you would have come across words like GPS, GLONASS, or Beidou. You may be familiar with GPS. But, what about GLONASS and Beidou? We are going to explore them in detail in this article. However, the crux of the matter is that all of the above are navigation systems owned by different countries.
Navigation Systems
In early days, human beings used to navigate oceans and vast stretches of lands with the help of the position of heavenly bodies such as the sun, moon, and the stars. Later, the learned how to make use of a compass. The electronic form of navigation that makes use of radio waves did not appear until the 1900s. It was not until the late 1900s that GPS came into the picture.
GPS
GPS stands for Global Positioning System. It was originally called Navstar GPS. The main purpose is to provide geolocation and time information to any GPS receiver in the world. What that means is that it enables any GPS capable device to pinpoint their location on the face of the Earth. The United States government is in ownership of this technology. And, its operation is in the hands of the United States Air Force. This system was originally developed in 1973 for the use of the military. Later, it was made open for public use sometime in the 1980s.
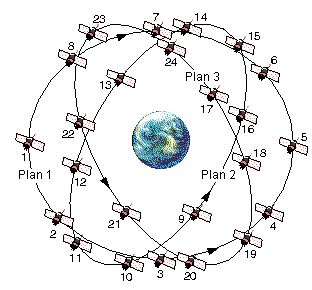
With a set of 31 satellites in orbit, the GPS system allows any receiver to accurately pinpoint their location up to 5 meters. Plans to upgrade the system are underway which would increase the accuracy to less than 30 centimetres. Smartphones make use of GPS for navigation. One advantage this technology has is that it can work without any internet connection or mobile network. However, the accuracy can see a tremendous increase by making use of mobile network and internet.
GLONASS
When the United States of America decides to develop a satellite navigation system, how can the Russian Federation stay behind? GLONASS is short for Globalnaya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema or Global Navigation Satellite System. It is the second system to provide global coverage after GPS. GLONASS obtained full coverage of Russia in the year 2010 and full global coverage in the year 2011. Under the Soviet Union, the GLONASS project didn’t have a bright future. And things were pretty dire after the fall of Soviet Union. However, in 2001, president Vladimir Putin increased funding and heavily focussed on the GLONASS project in order to complete it.
With development starting in 1976, this Soviet Union project has a cluster of 24 satellites in the orbit which provide accuracy of up to 4.5 meters. When paired with GPS, a device using GLONASS can show an accuracy of up to 2.5 meters. Plans are underway to upgrade and increase the accuracy to about 0.6 meters.
The pairing of GLONASS and GPS for use in a single device only happened when CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) systems were implemented in GLONASS satellites. Earlier they used to communicate using FMDA (Frequency Division Multiple Access) system. This allows them to use the same code but different frequencies in order to communicate with the satellites. However, GPS made use of CDMA where only one frequency but multiple codes are used to make contact with the satellites. Hence, there was a necessity to incorporate CDMA into GLONASS. Since GLONASS supports both FMDA and CDMA hardware architecture, it is costlier.
Beidou
When it comes to technological developments, China is not a country to place last in the race. Beidou or Beidou Navigation Satellite System is a Chinese satellite navigation system and is not much different to GPS and GLONASS. It has many systems of satellites aimed at serving various purposes.
The Beidou-1 is a cluster of 3 satellites targeted to provide position and navigation capabilities within China and neighbouring countries, albeit, it is severely limited. The Beidou-2 is a system of 35 satellites and is to become fully operational by 2020 when it would provide complete global coverage. It began offering services in the Asia-Pacific region in December 2012 with the help of 10 satellites already in the cluster in the orbit. Sources say that Beidou provides accuracy of up to 10 meters on its public service but close to centimetres or even millimetres on its encrypted service. Beidou has the potential to easily overtake GPS in the future in the field of global coverage and navigation according to various sources.
Which should you choose?
It doesn’t really matter. If it was earlier, you may have had to put in a lot of thought before buying a device with navigation capabilities. However, nowadays manufacturers tend to add more than one navigation system on devices to increase accuracy and reliability. For example, a device with both GPS and GLONASS would benefit from the service of GLONASS close to poles where there is lack of GPS service.
Verdict
It is just a matter of time before all three of them are able to provide unbridled global coverage of navigation facilities. In fact, there are more navigation systems out there. Europe has got its own and so does India. With so many in development, it is no more about which one is the best. Manufacturers of various devices have made sure to incorporate the salient points of more than one navigation system in their devices. This allows them to overcome the shortcomings of any one system. And with technological advancements, the navigation systems are inevitably going to improve. We can expect to see increased accuracy for civilian purposes and more coverage with better service.
Also read: Plan your next trip using Google Trips